Underscore
Summary
Avoid including an underscore character (_) in the identifier of
local variables, local functions, and parameters.
Default severity
Warning
Description
Don't use underscores in identifiers.
Rationale
This rule is recommended for the following reasons:
- Preserving the Discard Functionality: The underscore character (
_) is conventionally used for discards in C#. If a local variable, local function, or parameter is explicitly named_, it can shadow the discard feature within its scope. This means you might unintentionally be using a named variable instead of a discard, or you might be prevented from using discards as intended. This rule helps maintain the clarity and intended use of_for discards. - Adherence to .NET Coding Conventions: Using underscores within general
identifier names (e.g.,
local_variable,parameter_name) or as a standalone identifier for non-discard purposes is generally not in line with common .NET naming conventions, which favorcamelCasefor local variables and parameters. - Avoiding Ambiguity and Hungarian-like Prefixes: While some conventions
might use a leading underscore for private fields (e.g.,
_fieldName), applying this to local variables or parameters (e.g.,_param) can be seen as a form of Hungarian notation, which is generally discouraged in modern C# development. It can also lead to ambiguity with the discard_.
Discards
This analyzer ignores discards [1]. So it does not emit diagnostics for the following code:
// a standalone discard: ignored if no variable named '_' is in scope.
_ = "hello".Length;
// tuple
(int, int) NewPoint(int x, int y) => (x, y);
var (one, _) = NewPoint(1, 2);
// out parameter
void Out(out int x) => x = 3;
Out(out _);
// pattern matching (is)
if ("hello" is string _)
{
⋮
}
// pattern matching (switch)
switch ("hello")
{
case string _:
break;
⋮
}
Lambda parameters (checked)
This analyzer also emits diagnostics for lambda parameters [2]. So it emits diagnostics for the following code:
Func<int, int, int> f = (a, _) => a;
Lambda discard parameters (ignored)
This analyzer ignores lambda discard parameters [3] (a feature
introduced in C# 9.0). With lambda discard parameters, _ can be used multiple
times for parameters that are intentionally ignored.
So it does not emit diagnostics for the following code:
// lambda expression
Func<int, int, int> f = (_, _) => 42;
// anonymous function
var g = delegate (int _, int _) { return 0; };
🧷 Prior to C# 9.0, lambda expressions could not have multiple parameters named
_as it would cause a compile-time error due to duplicate parameter names.
How to distinguish between a discard and a regular parameter
As long as there is no variable named _ in the scope, _ is a discard.
Therefore, you can assign any value to it as follows:
_ = 42;
_ = "42";
Once you declare an identifier named _, it is no longer a discard and behaves
as a regular variable with a specific type. Assigning a value of the wrong type
(e.g., a string to an int variable _) causes a compile-time error due to
static typing.
To find out what _ is, see if an error occurs when you assign a different
type of value to it as follows:
// No error
public void LambdaDiscardParameters()
{
Func<int, int, int> f = (_, _) =>
{
// _ means a discard because there are no variables named '_'.
_ = "a";
return 0;
};
}
// Emits an error CS0029: Cannot implicitly convert type 'string' to 'int'
public void NoDiscardParameter()
{
Func<int, int> g = (_) =>
{
// '_' refers to the int parameter, not a discard.
_ = "a";
return 0;
};
}
Alternatively, you can determine what it is simply by using it. For example:
// Emits an error CS0103: The name '_' does not exist in the current context
public void LambdaDiscardParameters() {
Func<int, int, int> f = (_, _) =>
{
// _ means a discard because there are no variables named '_'.
return _;
};
}
public void NoDiscardParameter() {
Func<int, int> g = (_) =>
{
// '_' refers to the int parameter, not a discard.
return _;
};
}
Code fix
The code fix provides an option to replace the identifier with underscore if
the identifier contains only _ (a single underscore character). Otherwise, it
provides an option of eliminating underscores in the identifier and
concatenating words in the camel case style.
Example
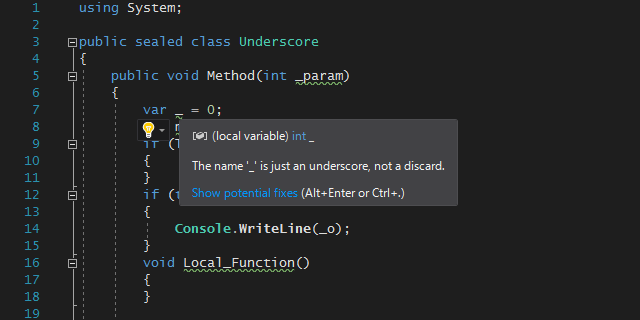
Diagnostic
public void Method(int _param)
{
var _ = 0;
var max_retry_count = 100;
if (TryToGet(out var return_value))
{
⋮
}
if (this is object _o)
{
⋮
}
void Local_Function()
{
⋮
}
⋮
Code fix
public void Method(int param)
{
var underscore = 0;
var maxRetryCount = 100;
if (TryToGet(out var returnValue))
{
⋮
}
if (this is object o)
{
⋮
}
void LocalFunction()
{
⋮
}
⋮
References
[1] Microsoft, C# Fundamentals, Discards