TypeClassParameter
Summary
Replace a System.Type parameter in a method or local function with a generic
type parameter when all arguments passed to it are typeof(…) expressions.
Default severity
Warning
Description
This analyzer identifies method or local function parameters of type
System.Type that are always invoked with typeof(…) expressions. In such
cases, the parameter can be safely replaced with a generic type parameter T,
which improves type safety and readability.
For example, consider the following code:
public void PrintTypes()
{
void Print(Type type)
{
Console.WriteLine(type.FullName);
}
Print(typeof(string));
Print(typeof(int));
⋮
All calls to Print use typeof(…). Therefore, you can refactor it using a
generic type parameter:
public void PrintTypes()
{
void Print<T>()
{
var type = typeof(T);
Console.WriteLine(type.FullName);
}
Print<string>();
Print<int>();
⋮
🚧 Restriction
In Visual Studio IDE, this analyzer only reports diagnostics for:
- Local functions
- Private methods
To analyze non-private methods, you must build the solution or run Analyze ➜ Run Code Analysis.
Excluded Cases
Static classes cannot be used with type parameters
This analyzer does not report diagnostics if any of the typeof(…)
arguments refer to a static class. Static classes cannot be used as type
arguments in C#, so replacing System.Type with a type parameter would be
invalid.
public static class SomeStaticClass;
// ❌ Skipped — static classes are not allowed as type arguments
Print(typeof(SomeStaticClass));
Method references prevent replacement
If the method or local function is passed as a method group (method reference)
to a delegate (e.g., Action<Type>), the analyzer does not report a
diagnostic.
void DoAction(Action<Type> action)
{
⋮
}
// ❌ Skipped — cannot convert generic method to Action<Type>
DoAction(Print);
Replacing Print(Type) with a generic method Print<T>() would
break this usage, so the analyzer conservatively ignores such cases.
Code fix
The code fix will:
- Replace the
Typeparameter with a generic type parameter. - Insert a local variable declaration
var … = typeof(T);at the beginning of the method or local function. - Update all call sites to use generic method syntax (e.g.,
DoSomething<string>()).
The new local variable will reuse the original parameter name for consistency.
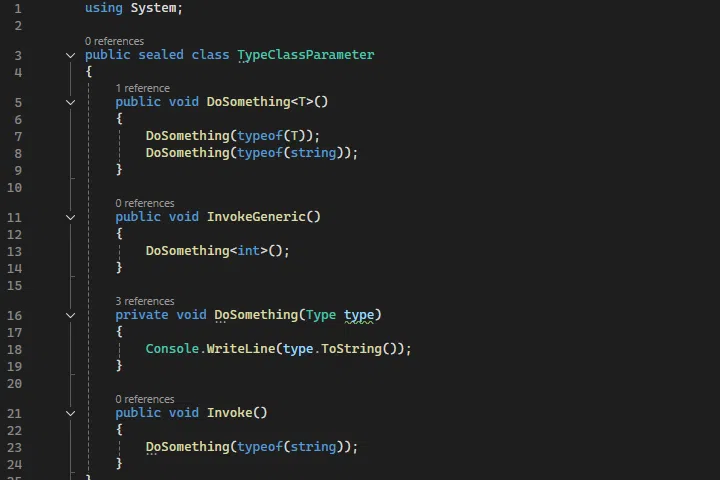
Example
Diagnostic
private void DoSomething(Type type)
{
⋮
}
public void Invoke()
{
DoSomething(typeof(string));
}
Code fix
private void DoSomething<T>()
{
var type = typeof(T);
⋮
}
public void Invoke()
{
DoSomething<string>();
}
🚨 Remarks
If the type already contains both
DoSomething(Type)andDoSomething<T>(), the code fix first renames the existingDoSomething<T>()method (e.g., toDoSomething_0<T>) to avoid a name conflict. Then it replaces theDoSomething(Type)method with the new generic version using the original name (DoSomething<T>()). This ensures that call sites referring toDoSomething(Type)can be safely updated to use the generic method.